Building Student Module for Large Language Models
Building Student Module for Large Language Models
Abstract
The current large language models (LLMs) mainly lacks this capability: autonomous learning capability. Also, we can not prepare all the data/knowledge in the world for LLMs.
We propose Learning In Conversation (LIC) to solve the problem to let human teach machine to refresh/expand its data/knowledge automatically by natural language conversation. LIC system is an AI system that contains many deep learning tasks. LIC system provide the natural language interface to let machine to learn new data/knowledge in conversation interacting with human automatically.
It is critical, but except for the developers of the AI system, others have no natural language interface to do this education for machine.
Based on large language models (LLMs) conversation ability, we train an additional intent recognition model to determine when the AI system need to learn new data/knowledge. We add a module for editing the training dataset of LLMs.
We propose the methods to implement our idea and discuss the reasons why we design these methods.
1. Introduction
The human learning procedure is the process of humans interacting with the world to determine whether they should learn new knowledge. For example, when humans are reading books or watching videos, Human beings will judge what knowledge should be learned into the brain from learning materials. If the learner cannot judge by himself, the human teacher will tell or emphasize the knowledge point.
In recent years, deep learning (DL) \cite{ref2} and GPT-based \cite{ref6} \cite{ref7} \cite{ref8} model have shown significant improvement on almost all the DL tasks. However there is currently a lack of a way for machines to learn automatically from humans in conversations. And we can not prepare all the data/knowledge in the world for LLMs.
In this paper we propose a framework of AI system, called LIC system. LIC system is based on LLMs and have the ability to learn in the conversation with human.
The LIC system has these modules:
1) LLMs to do conversation with human.
2) An intent recognition module to determine when and how to update data/knowledge in the system.
3) An data management module to update the training dataset.
2. The AI System
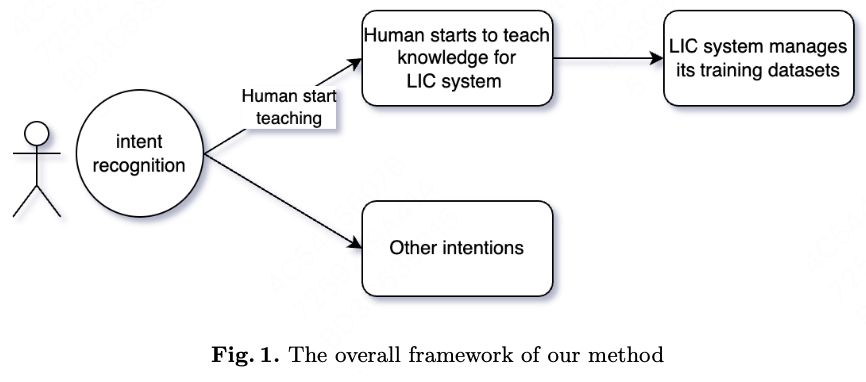
2.1 Common Conversation Module
To develop this module, we refer to ChatGPT \cite{ref11} \cite{ref12}.
2.2 Intent Recognition Module
This module determines when and how to start human-to-machine teaching.

This module has these functions:
1) Recognize the intention that human are teaching.
2) Not knowledgable, but know what is the knowledge.
3) Preparing the knowledge to the dataset format.
4) Determining when to call the data management module.
2.3 Data Management Module
This module receives requests from the LLMs and then updates the LLMs’ training datasets.

This module has these functions:
1) Finding the corresponding DL tasks that are related to the knowledge.
2) Finding the positions to add or update the data/knowledge in the training datasets of the DL tasks.
3. Discussion
The AI system under the deep learning framework is a powerful memory system. But we cannot prepare all the data in the world for the AI system to memorize, so we need to provide AI system with the ability to update knowledge autonomously.
Building a student module for LLMs takes a lot of engineering works and datasets preparing. And the goal of our work is to achieve better efficiency in data production. We are trying to find more efficient methods to prepare data for LLMs.
4. Related Work
There are great works \cite{ref3} \cite{ref4} \cite{ref5} that are solving the problem of autonomous machine intelligence.
Transformers-based models \cite{ref10} become the best models in most deep learning tasks. The transformers-based models also have the extremely excellent storage capabilities.
Data centric methods \cite{ref9} \cite{ref11} become the main methods to improve model performance. These data-centric methods become the cornerstones of industrial level NLP system.
Reward-based methods \cite{ref13} formulate the world into a reward based framework. And we need a lot of engineering works to make a reward based closed-loop system.
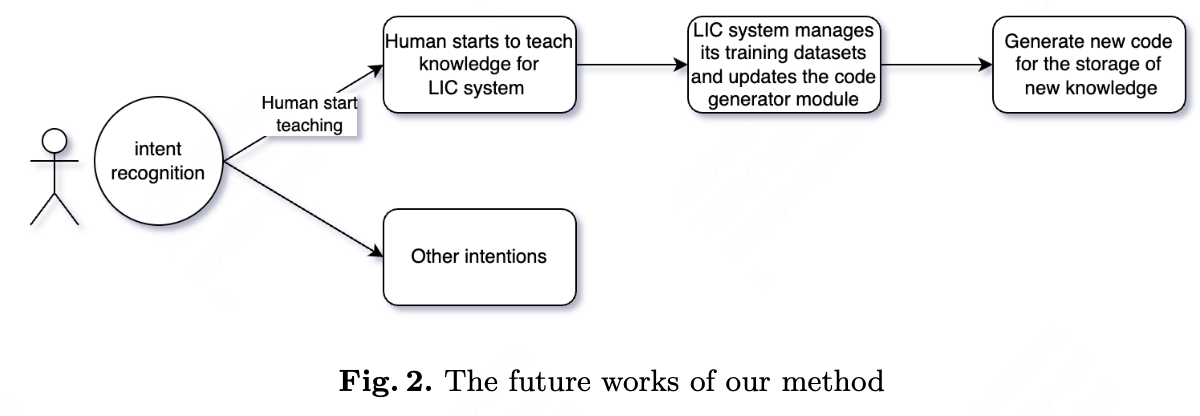
5. Future Works
The limitation of our proposed AI system is all the data/knowledge can only be stored under the defined formats or under the defined DL tasks. To overcome this limitation, we should let the AI system generate code to update its own code.
References
\bibitem{ref1}
Yu F, Zhang H, Wang B. Nature language reasoning, a survey[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.14725, 2023.
\bibitem{ref2}
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2012, 25: 1097-1105.
\bibitem{ref3}
LeCun Y. A path towards autonomous machine intelligence version 0.9. 2, 2022-06-27[J]. Open Review, 2022, 62(1).
\bibitem{ref4}
Assran M, Duval Q, Misra I, et al. Self-supervised learning from images with a joint-embedding predictive architecture[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2023: 15619-15629.
\bibitem{ref5}
Bardes A, Ponce J, LeCun Y. Mc-jepa: A joint-embedding predictive architecture for self-supervised learning of motion and content features[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.12698, 2023.
\bibitem{ref6}
Brown T, Mann B, Ryder N, et al. Language models are few-shot learners[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2020, 33: 1877-1901.
\bibitem{ref7}
Radford A, Narasimhan K, Salimans T, et al. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training[J]. 2018.
\bibitem{ref8}
Radford A, Wu J, Child R, et al. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners[J]. OpenAI blog, 2019, 1(8): 9.
\bibitem{ref9}
Zha D, Bhat Z P, Lai K H, et al. Data-centric artificial intelligence: A survey[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.10158, 2023.
\bibitem{ref10}
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Advances in neural information processing systems. 2017: 5998-6008.
\bibitem{ref11}
OpenAI (2023). GPT-4 Technical Report. ArXiv, abs/2303.08774.
\bibitem{ref12}
Ouyang L, Wu J, Jiang X, et al. Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.02155, 2022.
\bibitem{ref13}
Silver, David , et al. "Reward is enough." Artificial Intelligence 299.